|
Week Nine CalTRACK Update During week nine of CalTRACK, there were continued discussions on building qualification criteria and some introductory comments on hourly methods. The working group meeting will be held on Thursday, April 12th at 12:00 (PST). We will discuss:
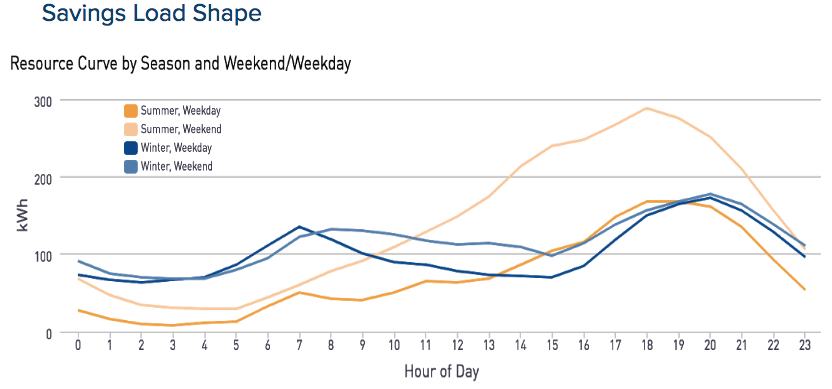
Hourly Methods Overview: Hourly methods are a new addition in CalTRACK 2.0 and were not in the first version of CalTRACK. This task involves testing various hourly modeling methods and recommending a standardized approach to hourly modeling, which can reveal the time value of energy efficiency. Importance of Hourly Methods:
Time Of Week and Temperature Models: To start the discussion of hourly methods, it is helpful to consider to existing open source tools. Lawrence Berkeley National Lab has developed an open source time of the week and temperature (TOWT) model to calculate hourly energy savings and is part of the RMV2.0 - LBNL M&V2.0 Tool. A TOWT model predicts hourly energy savings by utilizing hourly temperature data instead of daily or billing period HDD and CDD. Another is ECAM (ENERGY CHARTING & METRICS) developed by Bill Koran at SBW consulting. We look forward to discussion on the working group call about these approaches, and more to frame the approach to empirical tests for the CalTRACK 2.0 hourly methods. Final Note: It is important to remember that CalTRACK methods development is an iterative process. The finalized methods for CalTRACK 2.0, just like v. 1.0, will benefit from field deployment and may need to be revised in future years. We expect this process to result in improved and refined methods with successive iterations. Homework:
1 Comment
|
The purpose of this blog is to provide a high-level overview of CalTrack progress.
For a deeper understanding or to provide input on technical aspects of CalTrack, refer to the GitHub issues page (https://github.com/CalTRACK-2/caltrack/issues). Recordings
2019 CalTRACK Kick Off:
CalTRACK 2.0 July 19, 2018 June 28, 2018 June 7, 2018 May 24, 2018 May 3, 2018 April 12, 2018 March 29, 2018 March 15, 2018 March 1, 2018 February 15, 2018 February 1, 2018 Archives
March 2024
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
